Theory:
Let's start with the SIMPLE case:
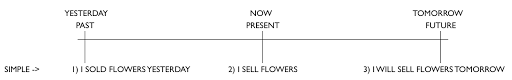 Number 1 is the PAST SIMPLE, 2 is the PRESENT SIMPLE and 3 is the FUTURE SIMPLE.
Number 1 is the PAST SIMPLE, 2 is the PRESENT SIMPLE and 3 is the FUTURE SIMPLE.
All three describe a general situation, and what is meant by general will become clearer as we go on.
The verb form used is the infinitive form without the TO for the present, the same for the future with the addition of WILL, and the past uses the past form of the verb.
Let's look at the CONTINUOUS case:
 Number 4 is the PAST CONTINUOUS, 5 is the PRESENT CONTINUOUS, and 6 is the FUTURE CONTINUOUS.
Number 4 is the PAST CONTINUOUS, 5 is the PRESENT CONTINUOUS, and 6 is the FUTURE CONTINUOUS.
All three refer to SPECIFIC TIMES and not general situations as with the simple cases.
All three refer to CONTINUOUS ACTIONS which means the action started before the specific time mentioned and will continue after the specific time mentioned, and this is sometimes called an incomplete action, or an unfinished action.
The verbs in all three cases end in ING.
All three need the verb TO BE, WAS for number 4, AM for number 5 and WILL BE for number 6.
Let's look at the PERFECT CONTINUOUS CASE:
 All three cases refer to DURATION - FOR 1 HOUR, and the reference for the duration is the specific time we used in the continuous case.
All three cases refer to DURATION - FOR 1 HOUR, and the reference for the duration is the specific time we used in the continuous case.
It is incorrect to use the continuous form for DURATION, and so you need to use the PERFECT CONTINUOUS case for that,
-
I AM WAITING for 1 hour. - is incorrect.
I HAVE BEEN WAITING for 1 hour, - is correct.
All three use the verb form ending in ING, because they again refer to actions which started before the referemce time and continued after the reference time.
All three need the verb TO BE - BEEN.
Let's look at the PERFECT SIMPLE case:
 The PERFECT SIMPLE cases all give the result of the PERFECT CONTINUOUS cases.
The PERFECT SIMPLE cases all give the result of the PERFECT CONTINUOUS cases.
For number 10), I had sold 5 flowers BECAUSE I had been selling flowers for 1 hour.
For 11), I have sold 5 flowers because I have been selling flowers for 1 hour, and
for 12), I will have sold 5 flowers because I will have been selling flowers for 1 hour.
All three cases use the past participle of the verb SOLD, with the auxilliaries HAD, HAVE and WILL HAVE.
Let's look at the case for the PRESENT:
 The present simple - I sell flowers is a general situation.
The present simple - I sell flowers is a general situation.
The present continuous - I am selling flowers now, relates to a specific moment, NOW,
The present perfect continuous uses that specific moment and relates to duration into the past with that moment as reference.
The present perfect simple case then gives the result of the present perfect continuous case
I have sold 5 flowers because I have been selling flowers for 1 hour.
Let's look at the case for the FUTURE:
 The future simple relates to a general situation.
The future simple relates to a general situation.
The future continuous relates to a specific time.
The future perfect relates to duration with the specific time as a reference.
Next week I will have been married for 25 years
The reference is next week, and the duration is 25 years and we used the future perfect.
Mary, who lives 2 hours away from the airport sees Sarah off on a 14 hour flight to Hong Kong. Sarah says,
"When you get home, I will be flying"� - future continuous.
"When you get home I will have been flying for 2 hours."� - Future perfect continuous
�"When you have dinner I will have landed."� - future perfect simple. (because I have been flying)
Let's look at the case for the PAST:
 The PAST SIMPLE relates to a general situation in the past,
The PAST SIMPLE relates to a general situation in the past,
I sold flowers yesterday.
The PAST CONTINUOUS relates to a situation in the past, but at a specific moment,
I was selling flowers when you called, or I was selling flowers at 6:00,
and the PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS relates to the duration of an event in the past, with a moment in the past as a reference,
I had been selling flowers for 1 hour when you called.
The PAST PERFECT SIMPLE then gives the result of the past perfect continuous,
I had sold 5 flowers when you called (past perfect simple) because I had been selling flowers for 1 hour when you called. (past perfect continuous).
The fuction of HAD is to put one event in the past before another event in the past.
"Yesterday I found the money I had lost last week."
One last thought:
 Imagine a little man who can only look backwards, standing as shown above.
Imagine a little man who can only look backwards, standing as shown above.
What he sees from his position in the past is the PAST PERFECT,
what he sees from his position in the present is the PRESENT PERFECT, and
what he sees from his position in the future is the FUTURE PERFECT.
This discussion gives the context of these verb tenses, but there are some other situations where these verb tenses are used which are not mentioned here. This information is meant to put these ideas into context, to show the most common way these ideas are used, and is not meant to be an analysis of every possible case that can occur.